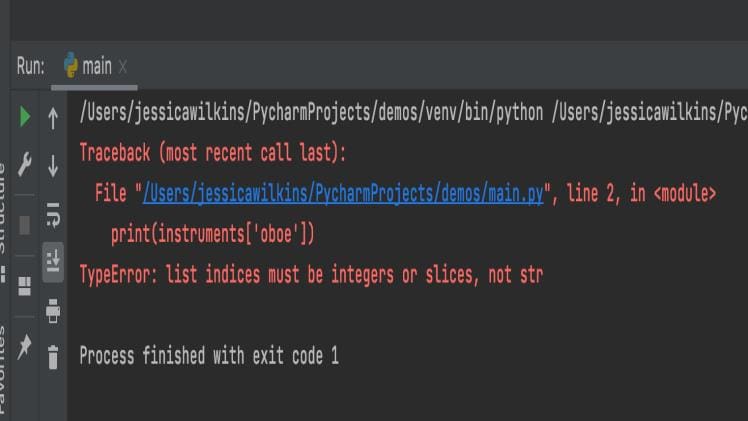
A list is a data structure in Python that is used to store multiple items in a single variable. A list index is an integer that is used to access a specific item within a list. In order to access a list item, the list index must be an integer or a slice, not a string. This article explains the importance of understanding list indices and the types of indices that can be used.
Understanding List Indices
List indices are used to access specific items within a list. In order to access a list item, the list index must be an integer or a slice, not a string. An integer list index is used to access an item at a specific place in the list. It is written in the form of a number inside square brackets. A slice is used to access a range of items in the list. It is written in the form of start:stop:step.
Types of List Indices
- Integer List Index – An integer list index is used to access an item at a specific place in the list. It is written in the form of a number inside square brackets. For example, if the list is [1,2,3,4,5], the integer list index for the item “3” is 2.
- Slice List Index – A slice is used to access a range of items in the list. It is written in the form of start:stop:step. For example, if the list is [1,2,3,4,5], the slice list index for the items “2,3,4” is 1:4:1.
In conclusion, understanding list indices is important in order to access specific list items. List indices must be integers or slices, not strings. This article has explained the importance of understanding list indices and the types of indices that can be used.